What is project cost control?
Project cost control involves estimating your projected budget, monitoring any of your projects’ expenses, and planning for unforeseen costs that may arise from risks in engineering and construction. As a result, cost control is also one of the most critical performance indicators for your projects.
Why is cost control so important?
Cost control for engineering and construction projects is imperative. It is not only monitoring or watching the cost but also performing analysis to make changes at the point of correction rather than waiting until the end of the project. At Anderson as part of our owner’s representation services we have found that with client satisfaction it is not that the budget was exceeded, it is that the client was not made aware of the budget being exceeded until the end of the project.
Good cost control must include: cost estimating, cost accounting, project cash flow, company cash flow, direct labor costing, and other tactics such as incentives, penalties, and profit-sharing.
Project cost control with earned value analysis
At Anderson, we have found great success using Earned Value Analysis for project cost control. Earned Value Analysis is a standard and often required technique used in the engineering and construction fields for analyzing project cost. Earned value analysis has three main components: planned value earned value, and actual cost. Using earned value analysis and the planned value, earned value, and actual cost, you can quickly know the status of your project and identify any required corrective actions.
Earned value analysis equations
There are several critical equations related to Earned Value Analysis that can help project managers when calculating their costs and schedule progress.
Inputs
- Planned Value: The forecasted spend against the project schedule. For this, we use Microsoft Project and Excel.
- Earned Value: This is the sum of the completed planned work. We track this by milestone using Asana and assign a percent complete value each task.
- Actual Cost: This is the actual cost of all work performed and includes: labor, expenses, subcontractors, etc.
Using the above inputs we are able to calculate the following values:
Cost Variance = Earned Value – Actual Cost
Schedule Variance = Earned Value – Planned Value
We report these values to the client bi-weekly as part of our project update and budget report. In addition to the above, when we act as the owners representative on facility improvement projects we also use the cost performance index and the schedule performance index.
Cost Performance Index = Earned Value / Actual Cost
Schedule Performance Index = Earned Value / Planned Value
In these equations, negative value means that the project is falling behind schedule or the cost is exceeding the planned budget. Positive means you are ahead of schedule or the earned value is above the planned value.
In our experience, if the cost performance index goes negative, it usually means the project has encountered either an unforeseen delay, technical issues, or a scope deficiency.
A full list of the earned value analysis equations are here.
Behind schedule but on-track
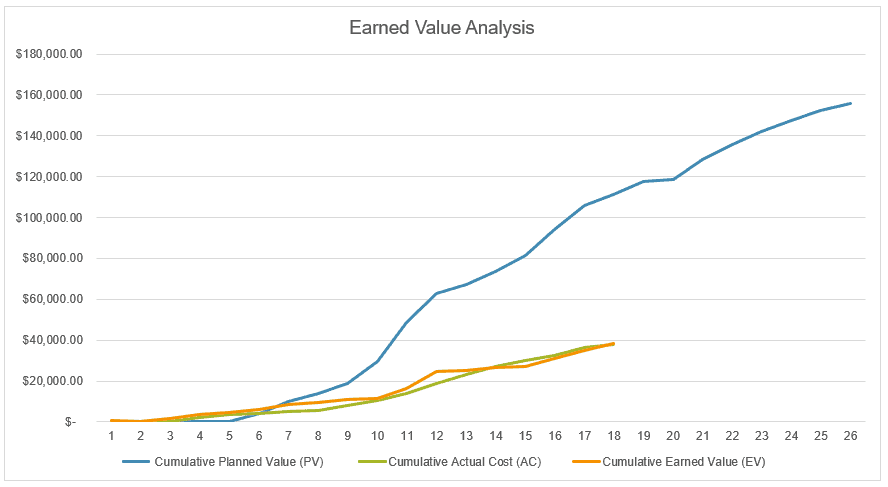
Earned value analysis is also helpful when the project is behind schedule due to unforeseen circumstances. For example on a recent project, we had a long-term stop work due to winter weather and unsafe working conditions. When it was time to start the project again, using earned value analysis we were able to show that while the project was significantly behind the planned value (blue line), the earned value and the actual cost were tracking appropriately and a change order was not required.
Use earned value analysis for your facility improvement projects
As the owner of your project, Earned Value Analysis give you a quick way to know the status and health of your project. To make it easier, included below are a couple of resources we use at Anderson.
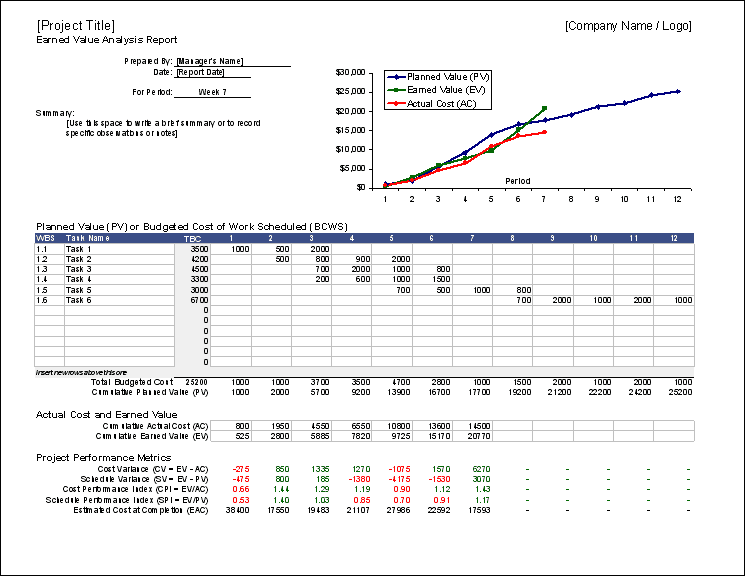
Earned Value Analysis Template
This template includes the necessities of the Earned Value Analysis equations to calculate your project’s performance over its course. This easy-to-use resource is simple: add your tasks, assigned costs, percentage completed, and actual costs for continuous calculation and detailed planning.